1. Cutting shape
1.1 Operation
(1) Samples
|
|
|
|
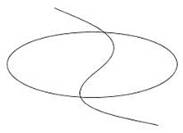
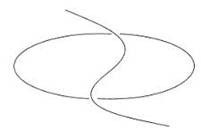
| Original shapes |
An ellipse cut by a cubic curve |
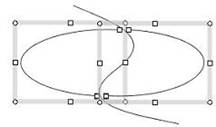
Displaying the selection boxes |
Figure 1.1 Sample of the operation
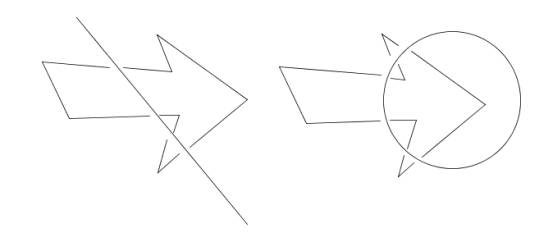
Figure 1.2 Sample of the operation
(2)The procedure of the operation
See => Figure 1.3
∙ Select a target shape and a cutting shape (cutter).
∙ If the "Cut both shapes? yes" button is selected, the both
shapes cut each other.
∙ Click the "Go" button, then the cutting operation will be performed
displaying the intersection points of the blue marks.
The Repeat button is enabled. Another cutting operation can be performed
by pressing the Repeat button.
1.2 Class CutShape
return=>page top
public class CutShape extends JDialog
|
Field
|
Description
|
action
|
CutShapeAction action
Sets the CutShapeAction.
|
|
messageLabel1
|
JLabel messageLabel1
Sets the label object on which the
showMessage methods displays a message.
|
|
messageLabel2
|
JLabel messageLabel2
Sets the label object on which the
showMessage methods displays a message.
The messageLabel1 and messageLabel2 are placed in the upper and lower.
When a message is long and is divided by \n, it will be displayed
on the upper and lower labels.
|
|
goButton
|
JButton goButton
The button object of "Go".
|
|
repeatButton
|
JButton repeatButton
The button object of "Repeat". |
|
cancelButton
|
JButton cancelButton
The button object of "Cancel". This button isn't used now.
|
|
selectPanel
|
JPanel selectPanel
The panel object of "cut both shapes? yes/no” buttons.
If the "yes/no" button are disabled, the title of the panel will be
displayed with gray. If the "yes/no" button are enabled, the the title will be
displayed with black.
|
|
yesButton
|
RadioButton yesButton
The button object of "yes"
|
|
noButton
|
JRadioButton noButton
The button object of "no"
|
|
shapeVector
|
Vector shapeVector
Stores the selected shapes.
|
|
Method
|
Description
|
|
Constructor
|
public CutShape()
Calls the following methods.
super(ObjectTable.getDrawMain(), "cut shape");
this.setName("cut shape");
this.action=new CutShapeAction(this);
this.createDialog();
|
|
createDialog
|
public void createDialog()
∙ Sets the dialog position at the left upper of the window.
∙ Adds the WindowListener to the dialog.
Before the window is closed,
the windowClosing method calls the closeDialogmethod.
∙ Adds the components to the dialog.
Upper row: the message label.
Middle row: The panel in which "Go" and "Repeat" buttons
are added.
Lower row: The panel of the "Cut both shapes?" label and the
Æ"yes" "no" buttons.
∙ Set the CutShapetAction to the "Go"
and "repeat" buttons as a ActionListener.
∙ Register the SelectionListener to
SelectionLS to be able to receive selected shapes.
selectionLS.addSelectionListener(this);
|
|
showDialog
|
public void showDialog(int commandId)
∙ Shows the dialog by setVisible method.
this.dialog.pack();
this.dialog.setVisible(true);
∙ If shapes are selected, then saves them to the shapeVector.
The selected shapes are checked whether they are appropriate or not
by the isSutable method.
If appropriate, then they are converted to new objects of
the MouseHitShape and the
MouseHitShape objects will be saved to the
shapeVector.
|
setSelectPanel
Enable
|
protected void setSelectPanelEnable(boolean enable)
Parameters:
enable - If true, then the text and the buttons on the
selectPanel are displayed with black.
if false, then they are displayed with light gray which shows the buttons are disabled.
|
|
showMessage
|
protected void showMessage(String message, Color color)
Parameter:
message - The message string.
color - The message color.
Processing:
Shows the message to the messageLabel.
|
|
getClickedShapes
|
public MouseHitShape[] getClickedShapes()
Returns all the MouseHitShape objects saved in the shapeVector.
This method is called by the CutShapeAction class.
|
|
selected
|
public void selected(SelectionEvent event)
Parameters:
event - SelectionEvent object.
Processing:
If a shape is selected by the mouse click in the SelectionLS,
then this method called.
This method checks whether the selected shape is appropriate or not by
isSuitable method. If appropriate, then this method creates a new object of the
MouseHitShape and saves it to the shapeVector.
This method shows a message according to the number of the received shapes.
∙ The number equals 1: The message which requires to select a cutting shape.
∙ The number is more than or equal to 2: The message of "Go or Cancel".
In addition, this method makes the goButton enabled
and calls the setSelectPanelEnable method.
this.goButton.setEnabled(true);
this.setSelectPanelEnable(true);
|
|
isSuitable
|
private boolean isSuitable(ShapeContainer container)
Checks whether the shape denoted by container is appropriate or not
for the cutting operation.
A shape with a text box and a group are inappropriate. |
|
isDuplicated
|
private int isDuplicated(ShapeContainer container)
Duplication check between a target shape and a cutter shape.
|
|
closeDialog
|
private void closeDialog()
Close the dialog.
• Remove temporary marks and strings on the drawing panel.
• Remove the SelectionListener
from SelectionLS.
|
|
windowClosing
|
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
Call the closeDialog method.
|
1.3 Class CutShapeAction
return=>page top
class CutShapeAction extends AbstractAction implements WindowListener
The main purpose of this class is the operation of cutting a shape.
|
Field
|
Description
|
dialog
|
CutShape dialog
Sets the CutShape object to this field.
|
|
Method
|
Description
|
| Constructor |
public CutShapeAction(CutShape dialog)
Sets the parameter to dialog field. |
|
actionPerformed
|
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
Executes the action processing of the clicked button.
∙ "Go" button
Calls the cutShapes method and the
endProcess method.
∙ "Repeat" button
Calls the repeatProcess method.
∙ "Cancel" button
Calls the closeDialog method.
|
| cutShapes |
private void cut()
∙ Calls the getIntersection method
and displays the blue marks at the intersection points.
The getIntersection calls the Curve2DUtil.getIntersectionPts method to calculates the intersection points between the target shape
and the cutting shape.
∙ Calls the cutContainer method to cut the target shape.
If the yesButton is selected,
then this method also cuts the cutting shape.
∙ Undo setup.
Calls the ContainerManager.undoSetupStart method
before cutting and calls the ContainerManager.undoSetupEnd method after cutting.
 => The undo support function of the ContainerManager.
=> The undo support function of the ContainerManager.
|
|
getIntersection
|
private CrossCurvePT[] getIntersection()
This method calls the Curve2DUtil.getIntersectionPts method
to calculates the intersection points.
If intersection points are found, then this method returns the
CrossCurvePT objects storing the intersection points,
and display blue marks at the intersection points.
|
|
getExchangedData
|
private CrossCurvePT[] getExchangedData(CrossCurvePT[] crossPTs)
This method exchanges the t1, t2 and the p1,p2 of the
CrossCurvePT object.
|
|
cutContainer
|
private ShapeContainer[] cutContainer(CrossCurvePT[] crossPTs, ShapeContainer
targetContainer)
Parameters:
crossPTs - The intersection points between the target shape and the cutting shape.
targetContainer - The shape to be cut.
Returns:
The array of new ShapeContainer objects of the cut shapes.
Processing:
∙ Calls the getCutParams method to get the curve parameters of the intersection (cutting) points
on the target shape.
The curve parameters arranged in ascending order.
∙ Calls the getTrimmedContainer method
to create cut shapes one by one.
∙ Registers the cut shapes to the ContainerManager.
|
|
getCutParams
|
private double[] getCutParams(Curve2D curve, double[] crossParams)
Parameters:
curve - The parametric curve of the target shape boundary.
crossParams - The parameters of the intersection points.
Returns:
The parameters representing cutting points.
Processing:
∙ Sorts the crossParams in ascendant order.
Let's denote the sorted crossParams as t0, t1, ..., tn-1 (t0<t1<...<tn-1).
∙ If the target shape has a open boundary, then returns the following parameters.
Returns ts, t0, t1, ..., tn-1, te. Here the ts is the start parameter of
the parametric curve, and the te is the end parameter. The [ts,t0],
[t0,t1],...[tn-1,te] represent the parameter intervals of new shapes to
be created by the cutting operation.
∙ If the target shape has a closed boundary, then returns the following parameters.
Returns t0, t1, ..., tn-1, t0. The [t0,t1],...[tn-1,t0] represent
the parameter intervals of new shapes to be created by the cutting operation.
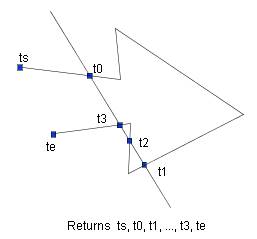
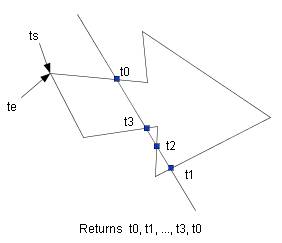
Figure_(a) The open boundary
Figure_(b) The closed boundary
|
getTrimmed
Container
|
private ShapeContainer getTrimmedContainer(ShapeContainer shapeContainer,
double t1, double t2)
Parameters:
shapeContainer - The shape to be cut.
t1, t2 - The parameter interval of a new shape to be created.
Returns:
A trimmed curve of the new shape to be created.
Processing:
∙ Calls the Curve2DUtil.trimCurve2D method
to cut the target shape boundary.
The case of t1>t2 is a special case corresponding to
[t3,t0] interval in Figure_(a). The [t3,t0] interval contains the start
point (ts) and the end point (te), so the trimmed curve of [t3,te] and
that of [ts,t0] must be connected into one curve. This processing is performed
by the trimCurve2D method.
∙ Changes the GeneralCurve2DE
of the trimmed curve to simpler form, if possible.
The trimmed curve is represented by the GeneralCurve2DE class. However,
if it is substantially a simpler form like a line, a polyline or a cubic
curve, it will be changed to Line2DE, Polyline2DE or CubicCureve2DE.
|
|
endProcess
|
private void endProcess()
Executes the ending process without closing dialog.
|
|
repeatProcess
|
private void repeatProcess()
Set the dialog its initial state in order to execute a next cutting operation.
|
|
closeDialog
|
private void closeDialog()
• Remove temporary marks and strings on the drawing panel.
• Remove the SelectionListener from
SelectionLS.
|
|
windowClosing
|
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
Calls the closeDialog method.
|
2. Connecting curves
return=>page top
The procedure
After the dialog opens, you have to select curves with clicking a mouse
and press "Go" button, then a new curve will be created by connecting
the selected curves on the condition that the new curve passes through the clicked points.
The rules of the operation
This function creates a new curve by connecting the curve intervals of the selected curves.
Each curve interval has to contain the corresponding clicked point inside.
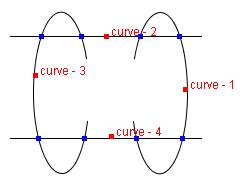
Let's denote the selected curves as C0, C1, C2,...Cn-1.
∙ If the intersection point is found between Ci-1 and Ci,
then this function connects Ci-1 with Ci via the intersection point
(Case (a) in the Figure 2.2).
∙ If no intersection point is found, then this function connects Ci-1 with Ci via a endpoint of one curve
and a point on other curve (Case (b), (c))
or via endpoints of Ci-1 and Ci (Case (d)).
In the case (b), the connection point on the Ci (blue mark) is the nearest point
from the end point of Ci-1.
The case (c) is similar to the case (b). In the case (b), (c) and (d),
the connection point of Ci-1 isn't equal to the connection point of Ci,
therefore the Ci is transformed so that the both connection points occupy the same location.
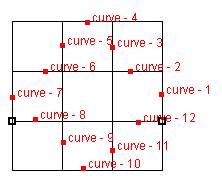
∙ If the multiple intersection points are found between Ci-1
and Ci and some kind of route panning technique is required to connect curves,
then this function outputs a error message (Case (e) in the Figure 2.3).
The reason is that such complex case can be easily avoided by the operation of cutting shape.
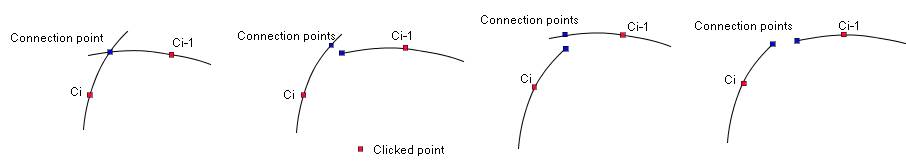
Case (a)
Case (b)
Case (c)
Case (d)
Figure 2.2 The cases of selecting the connection point
|
|
|

|
|
Case (e) Error
|
Case (f) Successful
|
Figure 2.3 Error case and successful case
2.1 Class ConnectCurves
return=>page top
|
Field
|
Description
|
action
|
ConnectCurvesAction action
Sets the ConnectCurvesAction to this field.
|
|
instructionLabel
|
JLabel instructionLabel
The label object displaying instruction.
|
|
messageLabel1
|
JLabel messageLabel1
Sets the label object on which the
showMessage methods displays a message.
|
|
messageLabel2
|
JLabel messageLabel2
Sets the label object on which the showMessage methods displays a message.
The messageLabel1 and messageLabel2 are placed in the upper and lower.
When a message is long and is divided by \n, it will be displayed
on the upper and lower labels.
|
|
goButton
|
JButton goButton:The button object of "Go".
|
|
repeatButton
|
JButton repeatButton
The button object of "Repeat".
|
|
shapeVector
|
Vector shapeVector
Stores the selected shapes.
|
| Method |
Description |
|
Constructor
|
public ConnectCurves()
Calls the following methods.
super(ObjectTable.getDrawMain(), "connect curves");
this.setName("connect curves");
this.action=new ConnectCurvesAction(this);
this.createDialog();
|
|
createDialog
|
public void createDialog()
∙ Sets the dialog position at the left upper of the window.
∙ Adds the WindowListener to the dialog.
Before the window is closed, the windowClosing method calls the
closeDialog method.
∙ Adds the components to the dialog.
Upper row: The instruction label.
Middle row: The message label.
Lower row: The panel of the "Go" and "Cancel" buttons.
∙ Add the ConnectCurvestAction
to the "Go" and "Cancel" buttons as a ActionListener.
∙ Register the SelectionListener to
SelectionLS to be able to receive selected shapes.
selectionLS.addSelectionListener(this);
|
|
showDialog
|
public void showDialog(int commandId)
∙ Shows the dialog by the following two lines.
this.pack();
this.setVisible(true);
|
|
showMessage
|
protected void showMessage(String message, Color color)
Shows the message to the messageLabel.
|
|
selected
|
public void selected(SelectionEvent event)
Parameters:
event - SelectionEvent object.
Processing:
If a shape is selected by the mouse click in the SelectionLS,
then this method called.
This method checks whether the selected shape is appropriate or not by
isSuitable method. If appropriate,
then this method creates a new object of the
MouseHitShape and saves it to the
shapeVector.
This method shows a message according to the number of the received shapes.
|
|
isSuitable
|
private boolean isSuitable(ShapeContainer container)
Checks whether the shape denoted by the container is appropriate or not for this operation.
Only a open curve is appropriate.
|
|
isDuplicated
|
private int isDuplicated(ShapeContainer container)
Duplication check between selected curves.
|
| closeDialog |
private void closeDialog()
• Remove temporary marks and strings on the drawing panel.
• Remove the SelectionListener
from SelectionLS.
|
|
getClickedShapes
|
public MouseHitShape[] getClickedShapes()
Returns all the MouseHitShape objects saved in the
shapeVector.
This method is called by the ConnectCurvesAction class.
|
2.2 Class ConnectCurvesAction
return=>page top
| Method |
Description |
| Constructor |
public ConnectCurvesAction(CutShape dialog)
Sets the parameter to dialog field. |
|
actionPerformed
|
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
Executes the action processing of the clicked button.
∙ "Go" button
Calls the connect method.
∙ "Cancel" button
Calls the closeDialog method.
|
| connect |
private int connect()
Returns: If the connecting operation fails, returns -1.
Processing:
∙ Calls the getConnectionPTs method and the
checkConnectionPTs method.
If the return value of the checkConnectionPTs
equals -1, then this method returns -1.
∙ Calls the createConnectedCurve method
to create a new object of the connected curve.
Registers the connected curve to the ContainerManager,
the the connected curve will be displayed on the canvas automatically.
∙ Undo setup.
Calls the ContainerManager.undoSetupStart method
before registering and calls the ContainerManager.undoSetupEnd method after registering.
 =>
The undo support function of the ContainerManager. =>
The undo support function of the ContainerManager.
|
|
getConnectionPTs
|
private void getConnectionPTs(Vector connectionVector)
Parameters:
connectionVector - Stores the Connection objects
which represent the connection points between the specified curves.
Processing:
∙ Retrieves the MouseHitShape objects by the
ConnectCurves.getClickedShapes method.
Let's denote the selected curves saved in the
MouseHitShape objects as C0, C1, C2,...Cn-1.
∙ Calls the calculateConnectionPTs method.
The calculateConnectionPTs method creates Connection objects which represent connection points between (Ci-1, Ci)
i=1,n-1, and saves the Connection objects to the connectionVector.
∙ Displays blue marks at the connection points by the
DrawShapeUtil.drawTempShape method.
|
calculate
ConnectionPTs
|
private void calculateConnectionPTs(ShapeContainer target1, ShapeContainer
target2, double tolerance, Vector connectionVector)
Parameters:
target1 - The curve Ci-1 shown in the Figure 2.2.
target2 - The curve Ci shown in the Figure 2.2.
tolerance - The error margin by which two points are regarded as a connection point.
connectionVector - Stores the Connection objects
which represent the connection points between the specified curves.
Processing:
This method calculates connection points between target1 and target2. Then it creates
Connection objects representing the connection points
and saves them to the connectionVector.
The connection points are calculated by the following two ways.
∙ Case (a) of Figure 2.2
Calculates intersection points by the Curve2DUti.getIntersectionPts.
In this case the intersection points are considered as connection points.
∙ Case (b), (c), (d) of Figure 2.2
This method calculates the nearest point on the target2
from the endpoint of the target1 and the nearest point on the target1 from the endpoint of the target2
by the Curve2DUti.getShortestLine method.
And this method chooses one from the nearest points, then the chosen nearest point
and the endpoint of the target1 or target2 are considered as connection points.
If the distance between the chosen nearest point and the endpoint is less than the tolerance (given by the parameter),
then they are stored in a single Connection object.
|
|
checkConnectionPTs
|
private int checkConnectionPTs()
Returns:
Returns -1, if the number of the specified curves is
two, those are (C0, C1), and more than two connection points are found.
Return -1, if the number of the specified curves is more
than two, those are (C0, C1, C2,...Cn-1, n≥3), and some couple of (Ci-1, Ci)
has multiple connection points.
|
|
getConnections
|
private Connection[] getConnections(ShapeContainer target1, ShapeContainer
target2, Vector connectionVector)
Parameters:
target1 - The curve Ci-1 shown in the Figure 2.2.
target2 - The curve Ci shown in the Figure 2.2.
connectionVector - Stores the Connection objects which represent the connection points between the target1 and
target2.
Returns:
The array of the Connection objects
which connect the target1 with the target2.
|
|
getConnections
|
private Connection[] getConnections(ShapeContainer target, Vector connectionVector)
Parameters:
target - The target curve.
connectionVector - Stores the Connection objects
which represent the connection points between the specified curves.
Returns:
The array of the Connection objects
which connect the target curve with any of the other curves.
|
createConnected
Curve
|
private ShapeContainer createConnectedCurve(Vector connectionVector)
Parameters:
connectionVector - Stores the Connection objects
which represent the connection points between the specified curves.
Returns:
The connected curve.
Processing:
The curves to be connected are given by the MouseHitShape objects
which are retrieved from the shapeVector
by the getCrikedShapes method of the
ConnectCurves.
∙ Calls the getCurveInterval method for each curve Ci.
The returned interval of the getCurveInterval method
defines the trimmed curve of Ci which is a part of the connected curve.
 =>
The Figure of the getCurveInterval. =>
The Figure of the getCurveInterval.
∙ Calls the Curve2DUti.trimCurve2D method
to create the trimmed curve of Ci.
∙ Call the createConnectedCurve2D method
to create the new object of the GeneralCurve2DE
representing the connected curve.
∙ Changes the GeneralCurve2DE of
the connected curve to simpler form, if possible.
If the connected curve is a polyline or a cubic curve, it will be
changed to Polyline2DE
or CubicCureve2DE.
∙ Stores the connected curve to the new object of the
ShapeElement and stores the
ShapeElement to the new object of the
ShapeContainer.
|
|
createConnectedCurve2D
|
private GeneralCurve2DE createConnectedCurve2D(GeneralCurve2DE trimmedCurve1,
GeneralCurve2DE trimmedCurve2)
Parameters:
trimmedCurve1 - The parametric trimmed curve Ci-1.
trimmedCurve2 - The parametric trimmed curve Ci.
Returns:
The connected curve which is a parametric curve of the
GeneralCurve2DE.
Processing:
∙ Changes the direction of the trimmedCurve1 and that of the trimmedCurve2
if necessary and connects the two curves.
∙ If the trimmedCurve1 and the trimmedCurve2 aren't continuous like the
case (b), (c), (d) in the Figure 2.2, this method calls the
ajustCurve method to make the two curve continuous
by modifying the trimmedCurve2.
|
|
getCurveInterval
|
private double[] getCurveInterval(ShapeContainer container, double clickedT,
Vector connectionVector)
Parameters:
container - The selected curve Ci.
clickedT - The curve parameter of the clicked point.
connectionVector - Stores the objects
which represent the connection points between the specified curves.
Returns:
The array storing the start parameter ts and end parameter te
of the interval which includes the clickedT.
The interval [ts, te] defines the trimmed curve of Ci which is a part of the connected curve.
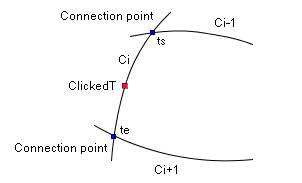
|
|
ajustCurve
|
private void ajustCurve(GeneralCurve2DE targetCurve, GeneralCurve2DE anchorCurve)
Parameters:
targetCurve - The curve Ci.
anchorCurve - The curve Ci-1.
Processing:
If the anchorCurve and the targetCurve aren't continuous like the
case (b), (c), (d) in the Figure 2.2,
then this method transforms the targetCurve to make the two curves continuous.
The transforming is performed by the Matrix2D.getRotationMatrix method
and the Curve2D.transform.
|
|
endProcess
|
private void endProcess()
This method is called when the OK button is pressed.
• Deselect the selected shapes in the drawing panel (canvas).
• Clear the shapeVector
• Remove the SelectionListener from the
SelectionLS.
|
|
repeatProcess
|
private void repeatProcess()
This method is called when the Repeat button is pressed.
• Deselect the selected shapes in the drawing panel (canvas).
• Disable the Go button and the Repeat button.
• Clear the shapeVector
• Remove the SelectionListener
from the SelectionLS.
|
|
closeDialog
|
private void closeDialog()
• Remove temporary marks and strings on the drawing panel.
• Remove the SelectionListener
from SelectionLS.
|
|
windowClosing
|
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
Calls the closeDialog method.
|
3. Class MouseHitShape
return=>page top
In the CutShape and the ConnectCurves classes,
the shapes to be manipulated are selected by the mouse clicks and the clicked points are important
for the manipulation.
The MouseHitShape class is used for storing the selected shape and the clicked point together.
|
Field
|
Description
|
|
shapeContainer
|
private ShapeContainer shapeContainer
The selected shape.
|
|
mousePosition
|
private Point2D mousePosition
The mouse position.
|
|
Method
|
Description
|
|
Constructor
|
public MouseHitShape(ShapeContainer shapeContainer, Point2D mousePosition)
|
|
getShapeContainer
|
public ShapeContainer getShapeContainer()
Returns the shapeContainer.
|
|
getMousePosition
|
public Point2D getMousePosition()
Returns the mousePosition.
|
|
getCurveParameter
|
public double getCurveParameter()
Returns the curve parameter of the mousePosition.
To get the curve parameter, this method calls the
Curve2DUtil.getShortestLine method.
|
getEndIndexClose
ToMouse |
public int getEndIndexCloseToMouse()
Returns the index (0/1) of the endpoint of the shapeContainer close
to the mouse position. |
|
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()